Lectures
Back : semi-conductor
Transistors
Check out
https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/transistor/tran_1.html
General categories
BJT - Bipolar Junction Transistor
(collector, emitter, base).
- current driven
- amplifies current
- moderate switching speed
- cheap
- always draw some power
- NPN and PNP
- most commonly used in
common-emitter mode.
- outputs an inverted signal.
- collector, emitter, base
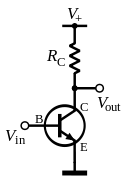
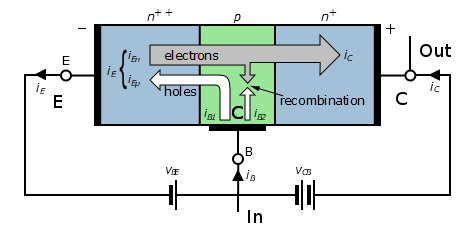 In common-emitter configuration, produces most power,
but inverts the input.
- inverted signaling actually makes logic easier to implement.
Transistors as amplifiers.
Transistor radio, cell phones, everything else in the world.
Transistors as switches by saturation.
FET - Field effect transistors
(source, drain, gate)
- voltage driven
- lower power draw
- more comlex +$
- several variations
MOS-FET (Metal Oxide Substrate)
In common-emitter configuration, produces most power,
but inverts the input.
- inverted signaling actually makes logic easier to implement.
Transistors as amplifiers.
Transistor radio, cell phones, everything else in the world.
Transistors as switches by saturation.
FET - Field effect transistors
(source, drain, gate)
- voltage driven
- lower power draw
- more comlex +$
- several variations
MOS-FET (Metal Oxide Substrate)
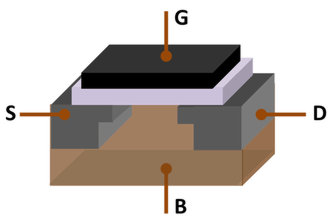 source : wikipedia
Layer (light color) between Gate substrate is insulating material.
- source(S), drain(D), gate(G), body(B) or substrate
# body exists primarily for physical support and overall biasing.
- very low power draw in inactive state.
- nMOSFET switch is on when + applied.
- pMOSFET switch is on when - applied.
- CMOS pairs a nMOSFET with a pMOSFET
- very low power draw (CMOS) except when switching
- designs from < 1 volt to 18 voltage.
- more expensive than BJT, especially CMOS
source : wikipedia
Layer (light color) between Gate substrate is insulating material.
- source(S), drain(D), gate(G), body(B) or substrate
# body exists primarily for physical support and overall biasing.
- very low power draw in inactive state.
- nMOSFET switch is on when + applied.
- pMOSFET switch is on when - applied.
- CMOS pairs a nMOSFET with a pMOSFET
- very low power draw (CMOS) except when switching
- designs from < 1 volt to 18 voltage.
- more expensive than BJT, especially CMOS
 N-MOS vs. CMOS early CPUs use NPN FET - N-MOS technology.
N-MOS switches draw power when in on state.
Newer use CMOS, pairs an NPN transistor with a PNP
2x transistors but power consumption greatly reduced.
Variety of customized transistors built on these model concepts.
Material other than original increases switching speed or current limits.
Gates
Basic transistor gates
NOT gates - input signal inverted.
Open collector and pull-up transistors.
N-MOS vs. CMOS early CPUs use NPN FET - N-MOS technology.
N-MOS switches draw power when in on state.
Newer use CMOS, pairs an NPN transistor with a PNP
2x transistors but power consumption greatly reduced.
Variety of customized transistors built on these model concepts.
Material other than original increases switching speed or current limits.
Gates
Basic transistor gates
NOT gates - input signal inverted.
Open collector and pull-up transistors.
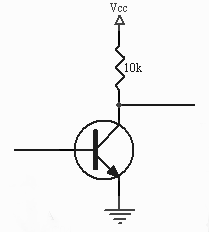 + on base yields - on collector.
- on base yields + on collector.
CMOS - static CMOS inverter
+ on base yields - on collector.
- on base yields + on collector.
CMOS - static CMOS inverter
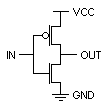 + on IN(gate) yields - on OUT.
- on IN(gate) yields + on OUT.
When output fed to input of a successive CMOS gate,
Power flows only long enough to charge or discharge gate.
Tri-State - 0, 1, disconnected
Graphics and symbols.
Gate graphics
Gate symbols +, *, !,',-, (+)
NOT - single transistor.
NAND - two transistors in series.
NOR - two transistors in parallel.
XOR - exclusive OR - either/or.
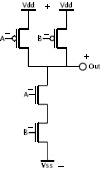
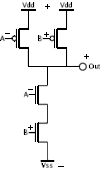
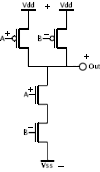
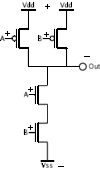
CMOS version of NAND ( + = 1, - = 0 )
(2* transistors)
+ on IN(gate) yields - on OUT.
- on IN(gate) yields + on OUT.
When output fed to input of a successive CMOS gate,
Power flows only long enough to charge or discharge gate.
Tri-State - 0, 1, disconnected
Graphics and symbols.
Gate graphics
Gate symbols +, *, !,',-, (+)
NOT - single transistor.
NAND - two transistors in series.
NOR - two transistors in parallel.
XOR - exclusive OR - either/or.
CMOS version of NAND ( + = 1, - = 0 )
(2* transistors)
| 0 0 -> 1 |
0 1 -> 1 |
1 0 -> 1 |
1 1 -> 0 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Circuits

 In common-emitter configuration, produces most power,
but inverts the input.
- inverted signaling actually makes logic easier to implement.
Transistors as amplifiers.
Transistor radio, cell phones, everything else in the world.
Transistors as switches by saturation.
FET - Field effect transistors
(source, drain, gate)
- voltage driven
- lower power draw
- more comlex +$
- several variations
MOS-FET (Metal Oxide Substrate)
In common-emitter configuration, produces most power,
but inverts the input.
- inverted signaling actually makes logic easier to implement.
Transistors as amplifiers.
Transistor radio, cell phones, everything else in the world.
Transistors as switches by saturation.
FET - Field effect transistors
(source, drain, gate)
- voltage driven
- lower power draw
- more comlex +$
- several variations
MOS-FET (Metal Oxide Substrate)
 source : wikipedia
Layer (light color) between Gate substrate is insulating material.
- source(S), drain(D), gate(G), body(B) or substrate
# body exists primarily for physical support and overall biasing.
- very low power draw in inactive state.
- nMOSFET switch is on when + applied.
- pMOSFET switch is on when - applied.
- CMOS pairs a nMOSFET with a pMOSFET
- very low power draw (CMOS) except when switching
- designs from < 1 volt to 18 voltage.
- more expensive than BJT, especially CMOS
source : wikipedia
Layer (light color) between Gate substrate is insulating material.
- source(S), drain(D), gate(G), body(B) or substrate
# body exists primarily for physical support and overall biasing.
- very low power draw in inactive state.
- nMOSFET switch is on when + applied.
- pMOSFET switch is on when - applied.
- CMOS pairs a nMOSFET with a pMOSFET
- very low power draw (CMOS) except when switching
- designs from < 1 volt to 18 voltage.
- more expensive than BJT, especially CMOS
 N-MOS vs. CMOS early CPUs use NPN FET - N-MOS technology.
N-MOS switches draw power when in on state.
Newer use CMOS, pairs an NPN transistor with a PNP
2x transistors but power consumption greatly reduced.
Variety of customized transistors built on these model concepts.
Material other than original increases switching speed or current limits.
Gates
Basic transistor gates
NOT gates - input signal inverted.
Open collector and pull-up transistors.
N-MOS vs. CMOS early CPUs use NPN FET - N-MOS technology.
N-MOS switches draw power when in on state.
Newer use CMOS, pairs an NPN transistor with a PNP
2x transistors but power consumption greatly reduced.
Variety of customized transistors built on these model concepts.
Material other than original increases switching speed or current limits.
Gates
Basic transistor gates
NOT gates - input signal inverted.
Open collector and pull-up transistors.
 + on base yields - on collector.
- on base yields + on collector.
CMOS - static CMOS inverter
+ on base yields - on collector.
- on base yields + on collector.
CMOS - static CMOS inverter
 + on IN(gate) yields - on OUT.
- on IN(gate) yields + on OUT.
When output fed to input of a successive CMOS gate,
Power flows only long enough to charge or discharge gate.
Tri-State - 0, 1, disconnected
Graphics and symbols.
Gate graphics
Gate symbols +, *, !,',-, (+)
NOT - single transistor.
NAND - two transistors in series.
NOR - two transistors in parallel.
XOR - exclusive OR - either/or.
CMOS version of NAND ( + = 1, - = 0 )
(2* transistors)
+ on IN(gate) yields - on OUT.
- on IN(gate) yields + on OUT.
When output fed to input of a successive CMOS gate,
Power flows only long enough to charge or discharge gate.
Tri-State - 0, 1, disconnected
Graphics and symbols.
Gate graphics
Gate symbols +, *, !,',-, (+)
NOT - single transistor.
NAND - two transistors in series.
NOR - two transistors in parallel.
XOR - exclusive OR - either/or.
CMOS version of NAND ( + = 1, - = 0 )
(2* transistors)



