 Source : wikipedia
Source : wikipedia
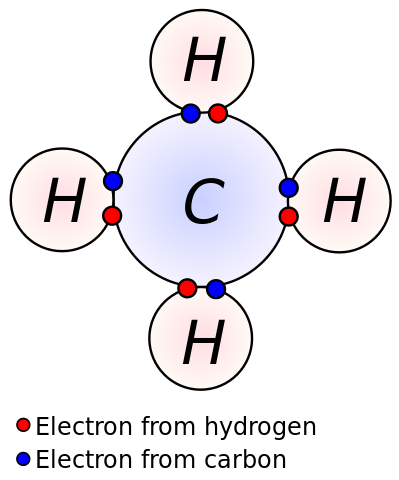 Source : DynaBlast [CC BY-SA 2.5 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5)], via Wikimedia Commons
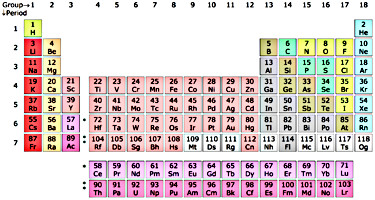
Semiconductor material
Silicon and Germanium - 4 electrons in outer shell.
Source : DynaBlast [CC BY-SA 2.5 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5)], via Wikimedia Commons
Semiconductor material
Silicon and Germanium - 4 electrons in outer shell.
NP - diode
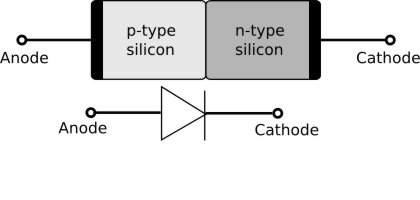 Source : wikipedia
Conventional Current flows from + to -
Electrons move from - to +
Semi-conductor depletion region. Why semi-conductors do what the do.
Source : wikipedia
Conventional Current flows from + to -
Electrons move from - to +
Semi-conductor depletion region. Why semi-conductors do what the do.
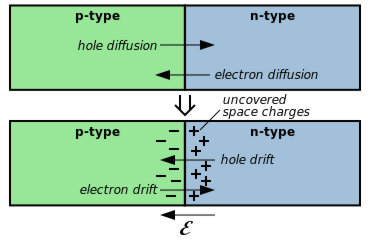 source : wikipedia
In unbiased (no power) state
Some electrons cross from N material to P material.
(and some holes cross over into the N material)
creating a neutral non-conducting region at junction
called a depletion region.
If forward bias, negative voltage applied to N and positive to P
Electrons move into the N material replacing the electrons
that crossed over into the P material.
Then move out to the positively charged connection.
Current flows.
In reverse bias, negative voltage applied to P material and positive to N
More electrons pulled from N material and added to p material
causing the depletion region to grow and become less conductive.
No current flow.
If reverse bias too large, the depletion gap breaks down.
Avalanche breakdown, usually destroy diode.
One way or check gate.
Special purpose
LED - when current crosses the junction, emits a photon of light.
Photo-diodes - converts photon to energy,
solar cells and photo sensors.
Zener diode - breaks down if reverse bias sufficiently large but
is usually not destroyed unless current extremely high.
Used for voltage control.
Avalanche diode - similar to Zener diode but capable of handling
much higher currents. Surge protection. (Physics slightly different).
Others.
Check out : electronics.howstuffworks.com/diode.htm
learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/diodes
NPN, PNP - transistors.
Very small electrical source causes a large current flow.
Valve that can be turned on and off.
learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/transistors
Transistors
source : wikipedia
In unbiased (no power) state
Some electrons cross from N material to P material.
(and some holes cross over into the N material)
creating a neutral non-conducting region at junction
called a depletion region.
If forward bias, negative voltage applied to N and positive to P
Electrons move into the N material replacing the electrons
that crossed over into the P material.
Then move out to the positively charged connection.
Current flows.
In reverse bias, negative voltage applied to P material and positive to N
More electrons pulled from N material and added to p material
causing the depletion region to grow and become less conductive.
No current flow.
If reverse bias too large, the depletion gap breaks down.
Avalanche breakdown, usually destroy diode.
One way or check gate.
Special purpose
LED - when current crosses the junction, emits a photon of light.
Photo-diodes - converts photon to energy,
solar cells and photo sensors.
Zener diode - breaks down if reverse bias sufficiently large but
is usually not destroyed unless current extremely high.
Used for voltage control.
Avalanche diode - similar to Zener diode but capable of handling
much higher currents. Surge protection. (Physics slightly different).
Others.
Check out : electronics.howstuffworks.com/diode.htm
learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/diodes
NPN, PNP - transistors.
Very small electrical source causes a large current flow.
Valve that can be turned on and off.
learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/transistors
Transistors