Assignment 8
Goals
The goal of this assignment is to work with the data processing and visualization in Python.
Instructions
You will be doing your work in Python for this assignment. You may
choose to work on this assignment on a hosted environment (e.g. tiger) or on your own local
installation of Jupyter and Python. You should use Python 3.10 or higher
for your work (although >= 3.8 is probably ok). To use tiger, use the
credentials you received. If you work remotely, make sure to download
the .py files to turn in. If you choose to work locally, Anaconda is the easiest way
to install and manage Python. If you work locally, you may launch
Jupyter Lab either from the Navigator application or via the
command-line as jupyter lab. You may need to install some
packages for this assignment: pandas, matplotlib, and altair. Use the
Navigator application or the command line
conda install pandas matplotlib altair to install them.
In this assignment, we will be working with data and visualizing it. We will revisit the port of entry data from Assignment 5, available from the United States Department of Transportation. However, instead of textual answers, we will create tables and visualizations to gain insight. We will use the same data that is available at http://faculty.cs.niu.edu/~dakoop/cs503-2022fa/a3/border-crossing.json. Note that you do not need to download or uncompress the data because pandas can load the url directly as a json file. This data has the following columns:
Port Name: a name for the port, often associated with its locationState: the state the port is located inPort Code: a unique numeric identifier for the portBorder: the country whose border the port is for (Canada or Mexico)Date: the month and year the data when the data was collectedMeasure: the type of conveyance/container/person being countedValue: the value of the measure for the specified month
Due Date
The assignment is due at 11:59pm on Friday, December 2.
Submission
You should submit the completed notebook file required for this
assignment on Blackboard. The
filename of the notebook should be a8.ipynb.
Details
Please make sure to follow instructions to receive full credit. Please document any shortcomings with your code. You may put the code for each part into one or more cells.
0. Name & Z-ID (5 pts)
The first cell of your notebook should be a markdown cell with a line for your name and a line for your Z-ID. If you wish to add other information (the assignment name, a description of the assignment), you may do so after these two lines.
1. Ports of Entry Statistics (20 pts)
First, we will use pandas to compute statistics about the ports of entries.
a. Most Bus Passengers (10 pts)
Load the dataset. Compute the month, port of
entry, and number of passengers when the most
Bus Passengers crossed the border. In this case, the month is the
Date column of the dataset which includes a month
and a year (so you do not need to aggregate anything
for this part).
Hints
- You can use pandas to load the data directly from the url above without downloading it.
- You can filter the data using bracket syntax or the query method.
- Statistical functions give the maximum value, but
idxversions of those functions give the index label. - Remember that
.locwill ensure that you index by the label.
b. Number of Ports per State (10 pts)
Redo Part 3b of Assignment 3 with pandas. In order words, count the number of ports for each state. Make sure that you count each unique port only once. You solution should be a Series with the states as labels and the counts as values.
Hints
- Remember to remove duplicates of the same port being reported at different times.
- You will need to use
groupbyand an aggregation operation to compute the counts.
2. Number of Crossings over Time
Next, let’s use visualization to examine trends in border crossings over time. We will use matplotlib (via pandas) for this.
a. Line Chart (15 pts)
Using matplotlib directly or via pandas, create a line chart visualization with two lines showing “Personal Vehicles” crossing over the months, one for crossings from Canada and the other from Mexico. You will need to use split-apply-combine again, but this time to sum the crossings for all of the ports of entry for each month. The lines should be different colors, and include a legend that indicates the values being shown by each line.
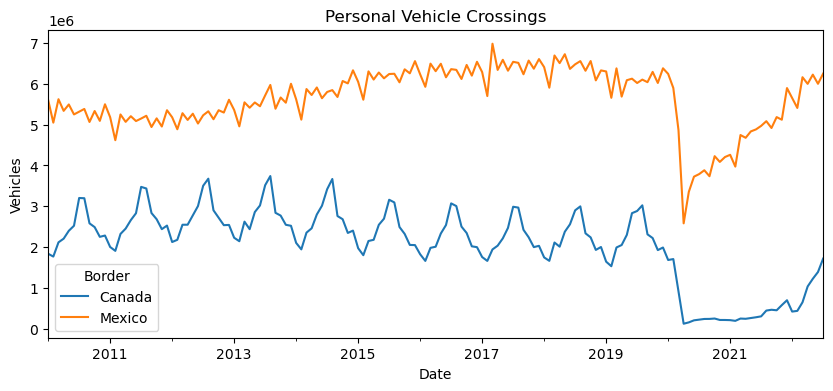
Hints:
- Using pandas, you can accomplish this plot in very few lines of code, but it can take some time and experimenting to find the correct set of calls.
unstackwill be quite useful if you set up your data correctly. Note that unstack can take a parameter that indicates the level of the index.
b. Stacked Bar Chart (20 pts)
Using matplotlib directly or via pandas’ plotting routines, create a visualization showing the average number of people crossing monthly for the four ports of entry in the state of Alaska using different modes of transportation. The modes we wish to examine are: Pedestrians, Train Passengers, Bus Passengers, and Personal Vehicle Passengers. Consider filtering the data to these ports and measures and then grouping by port, cmoputing the mean over the months. After the groupby, you can transform the data frame so that its rows are ports and its columns are the four modes of transportation. That data frame can be used directly by the pandas plot method. Display a legend.
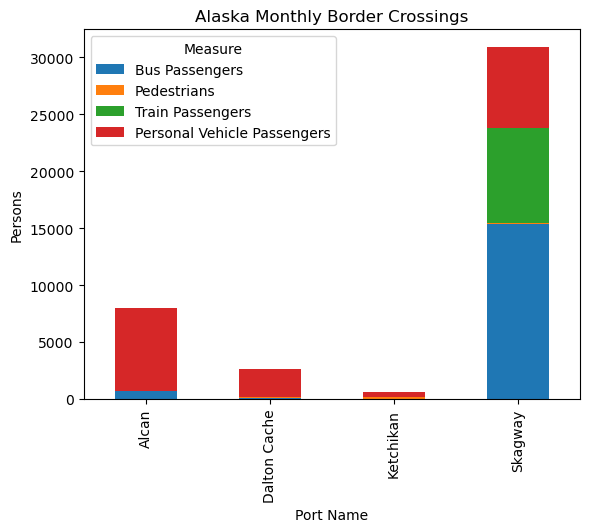
Hints:
- You are grouping by two columns.
unstackwill be quite useful if you set up your data correctly. Note that unstack can take a parameter that indicates the level of the index.
3. Port of Entry Comparison
Given the differences in vehicle crossings for different ports, we are interested to compare some of the ports that have the highest traffic over the time period from 2019 to present.
a. Port of Entry Dot Plots (15 pts)
Using altair, create nine dot plots showing the
number of personal vehicles crossing each of the
borders identified by the port codes
[901, 3801, 3004, 3802, 2504, 2402, 2506, 2304, 2305] for
the time from 2019-01-01 through the most recent data. This altair
example will be very useful as a reference, but make sure to cite it
if you adapt the code. There should be a dot plot for each of nine
ports; this is an instance of the small multiples visualization
technique. For extra credit, sort the facets so that the most heavily
trafficked ports (by average monthly vehicles) appear first.
Hints
- Make sure to filter the data to only keep the specified ports for the specified time.
- Remember that pandas will convert a string to a date if you want to compare dates.
- Altair’s faceting is useful to apply the same plot for each group of data.
b. [CSCI 503 Only] Brushing (15 pts)
Add interval brushing to the set of got plots such that a range of dots in one plot highlights the dots corresponding to the same date range in other plots. Show this highlight by changing the selected marks’ color.
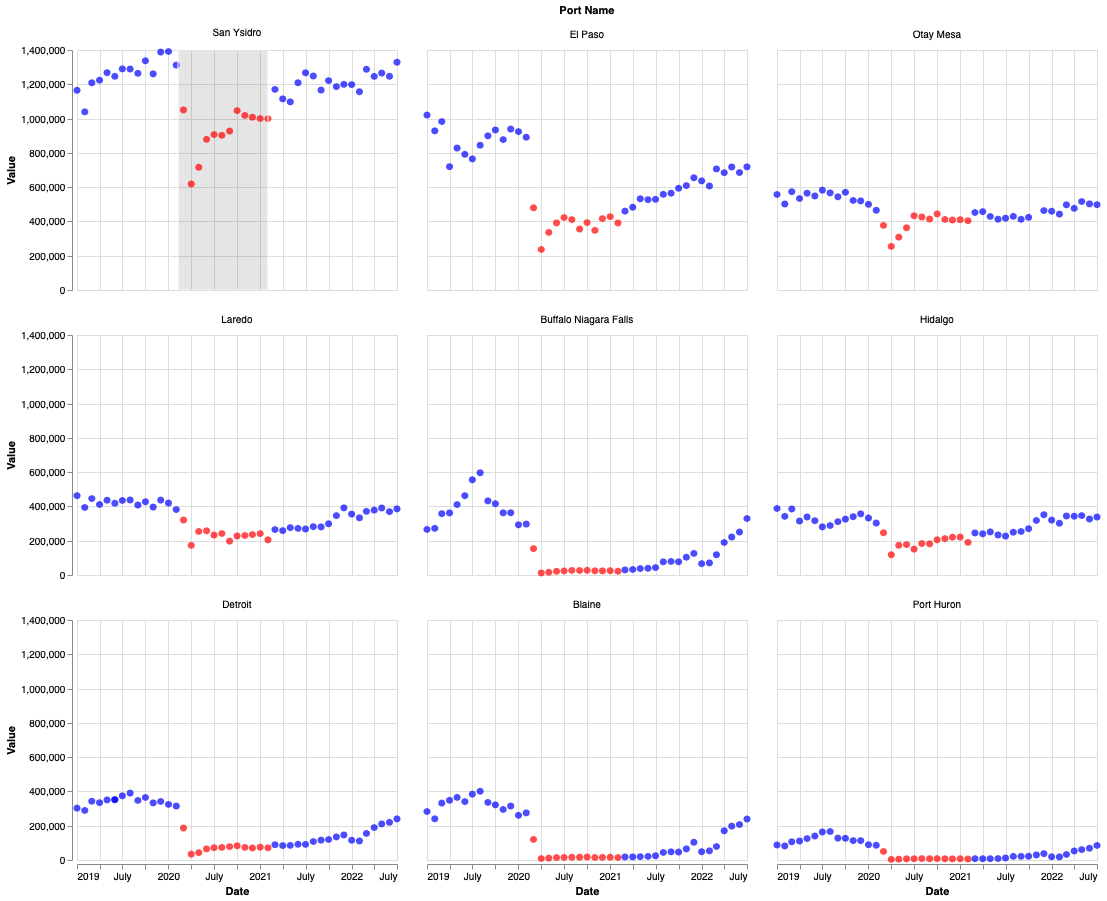
Hints
- Consult altair’s documentation on selections
- You need to make sure the selection uses the correct encoding, empty, and resolve settings.
- The fill color can be set using an
alt.condition.
Extra Credit
- [15 pts] CSCI 490 students may complete Part 3b.
- [5 pts] Sort the dot plots by the average traffic in Part 3a.
- [10 pts] Use altair to draw the plots in Part 2.