Back
Next
Detecting changes in signal/data stream is easier than detecting levels.
So, any protocol that increases the number of changes in a data stream
improves detection.
RLL - Run Length Limited (Huffman coding)
Encodes block of data bits on larger block of bits
to guarentee changes in signal level with in a limited span.
Data is encoded so that the number or "run" of consecutive zeros is limited.
Also limits number of consecutive one's to limit high frequency attenuation.
Cost - Increases the number of bits needed.
Generic example
Data RLL
000
001
00 010 010
01 011 011
100
10 101 101
11 110 110
111
When combined as a stream of bits,
At most 2 zeros or 4 ones next to each other.
Implementations of real RLL encoding is more complex.
Once data is encoded as RLL, any of the transmission/storage methods
may be used.
FM - Digital Frequency Modulation or Delay encoding
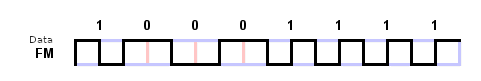 Delay encoding - (0,2) RLL
0 10
1 11
2x data stream.
Change at beginning of clock period.
Change in middle if data = 1
No change in middle if data = 0
Delay encoding is also known differential Manchester encoding.
MFM - Data is encoded so that there is a zero after any one and no more than
3 zeros in a row. Sometimes called (1,3)RLL
Delay encoding - (0,2) RLL
0 10
1 11
2x data stream.
Change at beginning of clock period.
Change in middle if data = 1
No change in middle if data = 0
Delay encoding is also known differential Manchester encoding.
MFM - Data is encoded so that there is a zero after any one and no more than
3 zeros in a row. Sometimes called (1,3)RLL
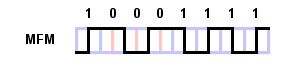 Used on floppies and early hard drives.
Notice there is always a change at the edge of the bit.
Like NRZI with a clock signal embedded.
Modified Frequency Modulation - MFM - form of FM combined with simple
RLL encoding.
Produced higher bit density that FM.
RLL(2,7) - encodes n bits of data on 2n bits. Most common on current storage.
But done in data bit groupings of 2, 3, or 4.
Guarantees that at least 2 consecutive 0s between bits
Guarantees that at most 7 consecutive 0s
RLL vs. MFM.
The number of actual transitions in the RLL signal allow for
1/3 smaller foot print when storing bit sequences.
Early hard drives 20 MB (MFM), 30 MB (RLL) - same physical drive.
Standard coding for hard drives for a long time.
Produced higher bit density that FM.
Used on floppies and earliest hard drives.
8b,10b - used with NRZ on wired Gigabit Ethernet.
DC free.
Used on floppies and early hard drives.
Notice there is always a change at the edge of the bit.
Like NRZI with a clock signal embedded.
Modified Frequency Modulation - MFM - form of FM combined with simple
RLL encoding.
Produced higher bit density that FM.
RLL(2,7) - encodes n bits of data on 2n bits. Most common on current storage.
But done in data bit groupings of 2, 3, or 4.
Guarantees that at least 2 consecutive 0s between bits
Guarantees that at most 7 consecutive 0s
RLL vs. MFM.
The number of actual transitions in the RLL signal allow for
1/3 smaller foot print when storing bit sequences.
Early hard drives 20 MB (MFM), 30 MB (RLL) - same physical drive.
Standard coding for hard drives for a long time.
Produced higher bit density that FM.
Used on floppies and earliest hard drives.
8b,10b - used with NRZ on wired Gigabit Ethernet.
DC free.
 Delay encoding - (0,2) RLL
0 10
1 11
2x data stream.
Change at beginning of clock period.
Change in middle if data = 1
No change in middle if data = 0
Delay encoding is also known differential Manchester encoding.
MFM - Data is encoded so that there is a zero after any one and no more than
3 zeros in a row. Sometimes called (1,3)RLL
Delay encoding - (0,2) RLL
0 10
1 11
2x data stream.
Change at beginning of clock period.
Change in middle if data = 1
No change in middle if data = 0
Delay encoding is also known differential Manchester encoding.
MFM - Data is encoded so that there is a zero after any one and no more than
3 zeros in a row. Sometimes called (1,3)RLL
 Used on floppies and early hard drives.
Notice there is always a change at the edge of the bit.
Like NRZI with a clock signal embedded.
Modified Frequency Modulation - MFM - form of FM combined with simple
RLL encoding.
Produced higher bit density that FM.
RLL(2,7) - encodes n bits of data on 2n bits. Most common on current storage.
But done in data bit groupings of 2, 3, or 4.
Guarantees that at least 2 consecutive 0s between bits
Guarantees that at most 7 consecutive 0s
RLL vs. MFM.
The number of actual transitions in the RLL signal allow for
1/3 smaller foot print when storing bit sequences.
Early hard drives 20 MB (MFM), 30 MB (RLL) - same physical drive.
Standard coding for hard drives for a long time.
Produced higher bit density that FM.
Used on floppies and earliest hard drives.
8b,10b - used with NRZ on wired Gigabit Ethernet.
DC free.
Used on floppies and early hard drives.
Notice there is always a change at the edge of the bit.
Like NRZI with a clock signal embedded.
Modified Frequency Modulation - MFM - form of FM combined with simple
RLL encoding.
Produced higher bit density that FM.
RLL(2,7) - encodes n bits of data on 2n bits. Most common on current storage.
But done in data bit groupings of 2, 3, or 4.
Guarantees that at least 2 consecutive 0s between bits
Guarantees that at most 7 consecutive 0s
RLL vs. MFM.
The number of actual transitions in the RLL signal allow for
1/3 smaller foot print when storing bit sequences.
Early hard drives 20 MB (MFM), 30 MB (RLL) - same physical drive.
Standard coding for hard drives for a long time.
Produced higher bit density that FM.
Used on floppies and earliest hard drives.
8b,10b - used with NRZ on wired Gigabit Ethernet.
DC free.