Back
Next
Technique : RZ - return to zero.
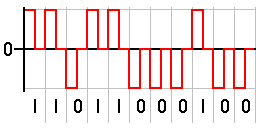 Provides a neutral non-transmitting condition.
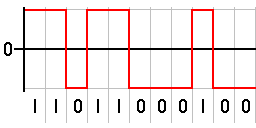
Technique : NRZ - non-return to zero.
Ones at one level and zeros at another.
Does not support a neutral (non-data) level.
Provides a neutral non-transmitting condition.
Technique : NRZ - non-return to zero.
Ones at one level and zeros at another.
Does not support a neutral (non-data) level.
 Highest density of single technology bit transferal.
System bus.
Problem :
Really long strings of all 1s or 0s loose distinction.
Level based signals can be inverted (zeros confused with ones)
Accumulated charge - if signal is electric and there is a long string
of a particular bit value, unbalanced electrical charges accumulate
at one end of the communication. This is sometimes called the DC
component.
Possible Solutions:
Assume sender and receiver synchronized.
Use very precise clocks and equipment.
Used with short-reach fiber optics. (?)
Provide second track or signal giving a timing measure.
Computer bus with clock line.
Use occasional re-sync signal (reserved bit sequence)
Used by modems (NON-DSL)
Transfer 7 or 8 bits of data at a time enclosed in start and stop bits.
High overhead but inexpensive technology.
RLL - run length limited.
Encodes set of bits on a larger bit set providing guarenteed transistions
with in a small time period.
Expands total number of bits transmitted/stored.
DC component - if a larger number one type of bit are transferred, it
is possible to build unequal charges between sender and receiver.
Accumulated charges balanced by requiring return ground line.
Certain RLL protocols produce sufficient changes to limit DC component.
But increases number of bits transmitted.
These solutions require more resources or expense.
Highest density of single technology bit transferal.
System bus.
Problem :
Really long strings of all 1s or 0s loose distinction.
Level based signals can be inverted (zeros confused with ones)
Accumulated charge - if signal is electric and there is a long string
of a particular bit value, unbalanced electrical charges accumulate
at one end of the communication. This is sometimes called the DC
component.
Possible Solutions:
Assume sender and receiver synchronized.
Use very precise clocks and equipment.
Used with short-reach fiber optics. (?)
Provide second track or signal giving a timing measure.
Computer bus with clock line.
Use occasional re-sync signal (reserved bit sequence)
Used by modems (NON-DSL)
Transfer 7 or 8 bits of data at a time enclosed in start and stop bits.
High overhead but inexpensive technology.
RLL - run length limited.
Encodes set of bits on a larger bit set providing guarenteed transistions
with in a small time period.
Expands total number of bits transmitted/stored.
DC component - if a larger number one type of bit are transferred, it
is possible to build unequal charges between sender and receiver.
Accumulated charges balanced by requiring return ground line.
Certain RLL protocols produce sufficient changes to limit DC component.
But increases number of bits transmitted.
These solutions require more resources or expense.
 Provides a neutral non-transmitting condition.
Technique : NRZ - non-return to zero.
Ones at one level and zeros at another.
Does not support a neutral (non-data) level.
Provides a neutral non-transmitting condition.
Technique : NRZ - non-return to zero.
Ones at one level and zeros at another.
Does not support a neutral (non-data) level.
 Highest density of single technology bit transferal.
System bus.
Problem :
Really long strings of all 1s or 0s loose distinction.
Level based signals can be inverted (zeros confused with ones)
Accumulated charge - if signal is electric and there is a long string
of a particular bit value, unbalanced electrical charges accumulate
at one end of the communication. This is sometimes called the DC
component.
Possible Solutions:
Assume sender and receiver synchronized.
Use very precise clocks and equipment.
Used with short-reach fiber optics. (?)
Provide second track or signal giving a timing measure.
Computer bus with clock line.
Use occasional re-sync signal (reserved bit sequence)
Used by modems (NON-DSL)
Transfer 7 or 8 bits of data at a time enclosed in start and stop bits.
High overhead but inexpensive technology.
RLL - run length limited.
Encodes set of bits on a larger bit set providing guarenteed transistions
with in a small time period.
Expands total number of bits transmitted/stored.
DC component - if a larger number one type of bit are transferred, it
is possible to build unequal charges between sender and receiver.
Accumulated charges balanced by requiring return ground line.
Certain RLL protocols produce sufficient changes to limit DC component.
But increases number of bits transmitted.
These solutions require more resources or expense.
Highest density of single technology bit transferal.
System bus.
Problem :
Really long strings of all 1s or 0s loose distinction.
Level based signals can be inverted (zeros confused with ones)
Accumulated charge - if signal is electric and there is a long string
of a particular bit value, unbalanced electrical charges accumulate
at one end of the communication. This is sometimes called the DC
component.
Possible Solutions:
Assume sender and receiver synchronized.
Use very precise clocks and equipment.
Used with short-reach fiber optics. (?)
Provide second track or signal giving a timing measure.
Computer bus with clock line.
Use occasional re-sync signal (reserved bit sequence)
Used by modems (NON-DSL)
Transfer 7 or 8 bits of data at a time enclosed in start and stop bits.
High overhead but inexpensive technology.
RLL - run length limited.
Encodes set of bits on a larger bit set providing guarenteed transistions
with in a small time period.
Expands total number of bits transmitted/stored.
DC component - if a larger number one type of bit are transferred, it
is possible to build unequal charges between sender and receiver.
Accumulated charges balanced by requiring return ground line.
Certain RLL protocols produce sufficient changes to limit DC component.
But increases number of bits transmitted.
These solutions require more resources or expense.