Test 2
Date & Time
Wednesday, November 8, 9:30-10:45am, PM 110
Overview
Test 2 will cover all material from the beginning of the semester through B-trees but will focus on material covered since Test 1. This material includes everything discussed in lectures and covered in assignments. You should know concepts (e.g. what an AVL tree is, how heap insertion works) as well as syntax. You may be asked to write, analyze, and/or debug code.
Format
- Multiple Choice
- Free Response
Topics
- Trees
- Binary Trees
- Tree Traversals
- Binary Search Trees
- AVL Trees
- Red-Black Trees
- Heaps
- B-Trees
- Node Insertion
- Node Deletion
- Tree Balancing (Rotations & Recoloring)
Example Types of Free-Response Questions
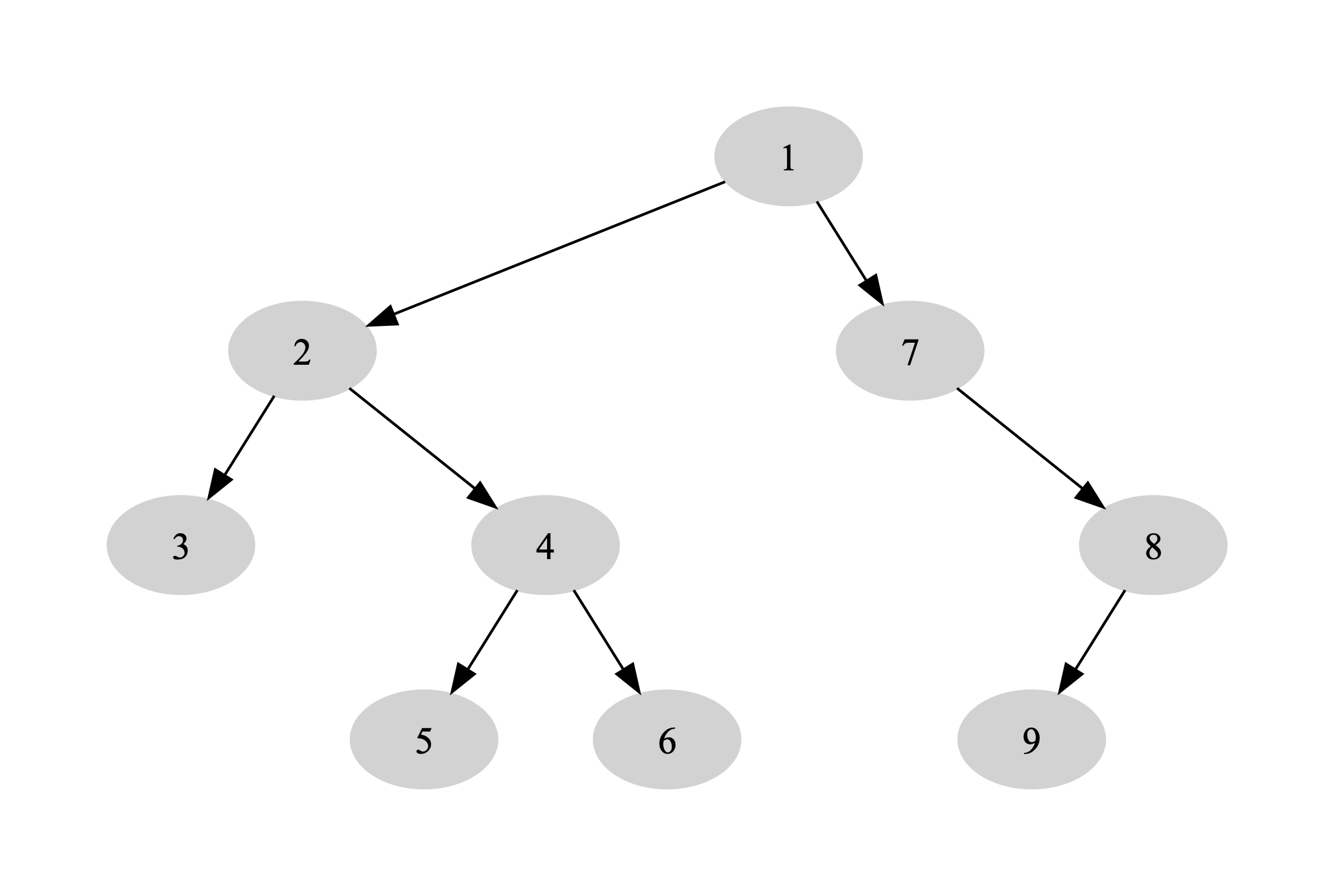
- Identify the root node of the above tree.
- Circle all the leaf nodes in the above tree.
- Calculate the height of the above tree.
- Compute the pre-order traversal of the above tree.
- Write code to count the number of leaf nodes in a binary tree.
- Write code to insert a new value into an existing binary search
tree. Assume the root node is named
rootand each node has avaluefield as well asleftandrightpointers to subtrees. - Why are AVL Trees and Red-Black trees an improvement over binary search trees?
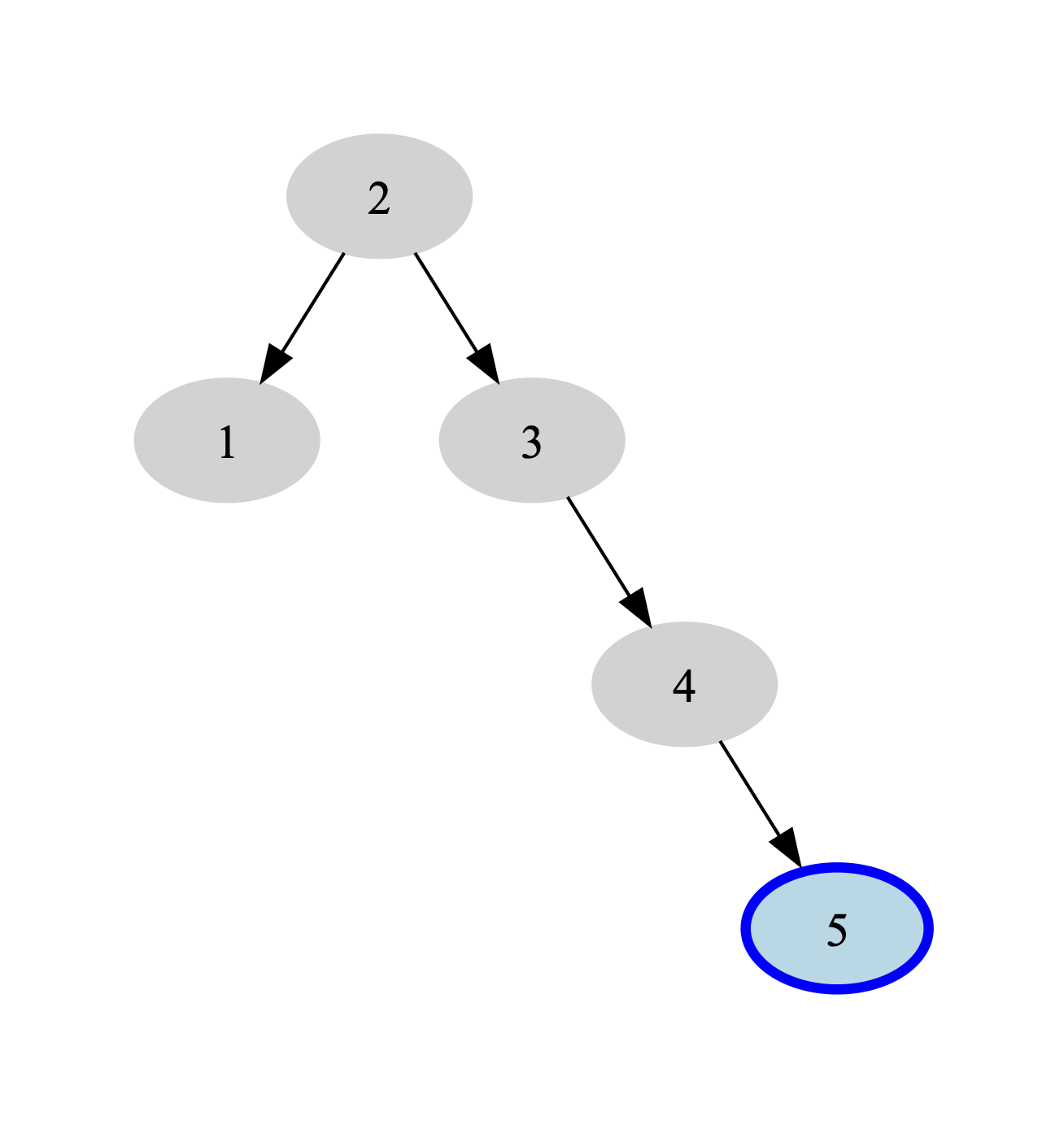
- Which case is the above AVL tree in after inserting 5?
- Which rotation(s) will be required to fix the above AVL tree?
- What is the difference between a min-heap and a max-heap?
- What are the two key properties that need to be maintained in a heap?
- Describe how you can use a max-heap to obtain a sorted array in-place.
- What type of operations are B-Trees designed to minimize?
- When deleting a value from a B-Tree, when do nodes need to be merged?