Back
Lectures
See nested raid on Wikipedia
Also PCGuide https://www.pcguide.com/ref/hdd/perf/raid/levels/mult.htm
Primary advantage of nested raid is that of extremely high data throughput
of level 0 or 3 while having the data protection of level 1 or 5.
Mostly Raid zero (true redundancy) combined with one of the other raid levels.
Raid level
01 or 0 and 1
10 or 1 and 0
Combines 0 and 1.
Still need 2X disks.
Raid 0+1
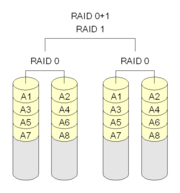 Data striped across multiple disks
Then duplicated on second set of disks.
File may cross several disks and allow for parallel access.
Failure of one drive causes system to act as straight Raid 0 until fixed.
Good fault tolerance and recovery.
Better(?) support for accessing different files at same time.
Raid 1+0
Data striped across multiple disks
Then duplicated on second set of disks.
File may cross several disks and allow for parallel access.
Failure of one drive causes system to act as straight Raid 0 until fixed.
Good fault tolerance and recovery.
Better(?) support for accessing different files at same time.
Raid 1+0
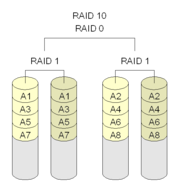 Disks paired off and mirrored.
Additional pairs added.
Better fault tolerance and recovery than 01.
Can support parallel access of both individual files and of multiple
files.
Very high read access.
Better(?) support for accessing single file quicker.
Because of the doubling of discs, scaling to large system prohibitive.
Placement of raid controllers provides the distinction between 10 and 01,
if single controller used, differences slight.
Raid 30 (sometimes called 53)
Raid 3 with redundant disks.
Raid 50
Each "disk" in the raid 0 model is a set of raid 5 disks.
Has speed of raid 0 and protection raid 5
****
Raid 51
Disks paired off and mirrored.
Additional pairs added.
Better fault tolerance and recovery than 01.
Can support parallel access of both individual files and of multiple
files.
Very high read access.
Better(?) support for accessing single file quicker.
Because of the doubling of discs, scaling to large system prohibitive.
Placement of raid controllers provides the distinction between 10 and 01,
if single controller used, differences slight.
Raid 30 (sometimes called 53)
Raid 3 with redundant disks.
Raid 50
Each "disk" in the raid 0 model is a set of raid 5 disks.
Has speed of raid 0 and protection raid 5
****
Raid 51
 Data striped across multiple disks
Then duplicated on second set of disks.
File may cross several disks and allow for parallel access.
Failure of one drive causes system to act as straight Raid 0 until fixed.
Good fault tolerance and recovery.
Better(?) support for accessing different files at same time.
Raid 1+0
Data striped across multiple disks
Then duplicated on second set of disks.
File may cross several disks and allow for parallel access.
Failure of one drive causes system to act as straight Raid 0 until fixed.
Good fault tolerance and recovery.
Better(?) support for accessing different files at same time.
Raid 1+0
 Disks paired off and mirrored.
Additional pairs added.
Better fault tolerance and recovery than 01.
Can support parallel access of both individual files and of multiple
files.
Very high read access.
Better(?) support for accessing single file quicker.
Because of the doubling of discs, scaling to large system prohibitive.
Placement of raid controllers provides the distinction between 10 and 01,
if single controller used, differences slight.
Raid 30 (sometimes called 53)
Raid 3 with redundant disks.
Raid 50
Each "disk" in the raid 0 model is a set of raid 5 disks.
Has speed of raid 0 and protection raid 5
****
Raid 51
Disks paired off and mirrored.
Additional pairs added.
Better fault tolerance and recovery than 01.
Can support parallel access of both individual files and of multiple
files.
Very high read access.
Better(?) support for accessing single file quicker.
Because of the doubling of discs, scaling to large system prohibitive.
Placement of raid controllers provides the distinction between 10 and 01,
if single controller used, differences slight.
Raid 30 (sometimes called 53)
Raid 3 with redundant disks.
Raid 50
Each "disk" in the raid 0 model is a set of raid 5 disks.
Has speed of raid 0 and protection raid 5
****
Raid 51