Lectures
Next
Calculating circuits
Comparator - compares two sets of values
a. equality detector - equal or not equal - cluster of XOR gates.
b. magnitude detector - which value is larger or if equal.
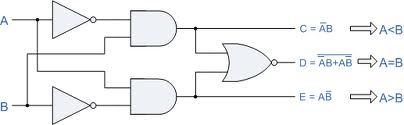 1-bit comparator - 5 gates.
Found at https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws
Another online electronics tutorial site.
4-bit comparator - 53 gates.
Multi-bit comparators more complex.
Alternative :
Take twos-comp of B
Add A and -B
resulting in positive, 0, or negative value.
Test CPU flags Z and N
Uses fewer gates but may take longer.
Also adder more flexible circuit.
Comparator - much faster, but more expensive customized circuit.
Add/subtract - 'cheaper' uses existing general purpose adder circuits
and software.
Shifter.
a. Shifts all bits making up a memory unit.
b. Multiply or divide by 2
c. Daisy chained.
d. LSL(R) ASL(R) ROL(R)
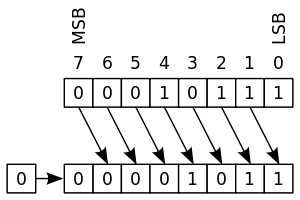
Logical shift -
zero shifted in
bit shifted out ignored
software and hardware implementations differ.
1-bit comparator - 5 gates.
Found at https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws
Another online electronics tutorial site.
4-bit comparator - 53 gates.
Multi-bit comparators more complex.
Alternative :
Take twos-comp of B
Add A and -B
resulting in positive, 0, or negative value.
Test CPU flags Z and N
Uses fewer gates but may take longer.
Also adder more flexible circuit.
Comparator - much faster, but more expensive customized circuit.
Add/subtract - 'cheaper' uses existing general purpose adder circuits
and software.
Shifter.
a. Shifts all bits making up a memory unit.
b. Multiply or divide by 2
c. Daisy chained.
d. LSL(R) ASL(R) ROL(R)
Logical shift -
zero shifted in
bit shifted out ignored
software and hardware implementations differ.
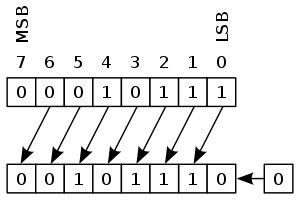
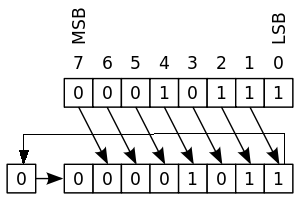
 Roll shift - ROR ROL - unsigned multiply/divide
Variation of circular and logical shifts, adds use of carry/borrow bit.
Shifted in and out between register and carry flag
Or bit shifted out is shifted in at other end. fairly rare.
* Unsigned integer mul/divide.
Roll shift - ROR ROL - unsigned multiply/divide
Variation of circular and logical shifts, adds use of carry/borrow bit.
Shifted in and out between register and carry flag
Or bit shifted out is shifted in at other end. fairly rare.
* Unsigned integer mul/divide.
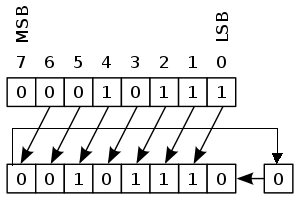
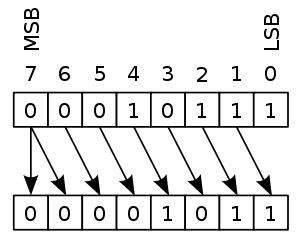
 Arithmetic shift - signed multiply/divide
zero shifted in (or carry flag on some systems)
high bit (sign) kept as is
2nd highest bit -> overflow
# If carry flag zeroed before shift,
circular shift can be used for arithmetic shift.
Arithmetic shift - signed multiply/divide
zero shifted in (or carry flag on some systems)
high bit (sign) kept as is
2nd highest bit -> overflow
# If carry flag zeroed before shift,
circular shift can be used for arithmetic shift.

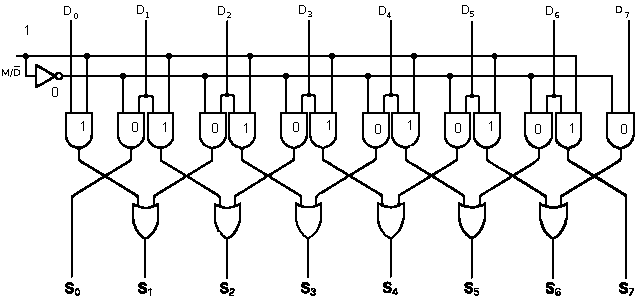
 Barrel shifter.
provides the ability to multiple shifts in a single action.
Commonly used in hardware floating point math to align significands
in single clock cycle.
Logical shift
Barrel shifter.
provides the ability to multiple shifts in a single action.
Commonly used in hardware floating point math to align significands
in single clock cycle.
Logical shift
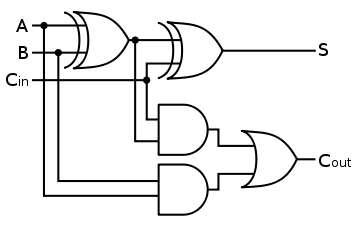
 Calculating Circuits - Adder
a. Half-adder - adds 1 bit from each number together
Calculating Circuits - Adder
a. Half-adder - adds 1 bit from each number together
b. Full-adder - adds bits with carry from lower bits.
i. Half adders daisy chained.
Graphic License
|
| A | B | Cin | | | Sum | Cout |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | | | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | | | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | | | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | | | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | | | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | | | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | | | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | | | 1 | 1 |
|
A series of full-adders are daisy chained together (16, 32, 64) to create a
numeric adder.
Adder circuit complexity is linear. 32 bit adder requires 32 full adders.
 1-bit comparator - 5 gates.
Found at https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws
Another online electronics tutorial site.
4-bit comparator - 53 gates.
Multi-bit comparators more complex.
Alternative :
Take twos-comp of B
Add A and -B
resulting in positive, 0, or negative value.
Test CPU flags Z and N
Uses fewer gates but may take longer.
Also adder more flexible circuit.
Comparator - much faster, but more expensive customized circuit.
Add/subtract - 'cheaper' uses existing general purpose adder circuits
and software.
Shifter.
a. Shifts all bits making up a memory unit.
b. Multiply or divide by 2
c. Daisy chained.
d. LSL(R) ASL(R) ROL(R)
Logical shift -
zero shifted in
bit shifted out ignored
software and hardware implementations differ.
1-bit comparator - 5 gates.
Found at https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws
Another online electronics tutorial site.
4-bit comparator - 53 gates.
Multi-bit comparators more complex.
Alternative :
Take twos-comp of B
Add A and -B
resulting in positive, 0, or negative value.
Test CPU flags Z and N
Uses fewer gates but may take longer.
Also adder more flexible circuit.
Comparator - much faster, but more expensive customized circuit.
Add/subtract - 'cheaper' uses existing general purpose adder circuits
and software.
Shifter.
a. Shifts all bits making up a memory unit.
b. Multiply or divide by 2
c. Daisy chained.
d. LSL(R) ASL(R) ROL(R)
Logical shift -
zero shifted in
bit shifted out ignored
software and hardware implementations differ.

 Roll shift - ROR ROL - unsigned multiply/divide
Variation of circular and logical shifts, adds use of carry/borrow bit.
Shifted in and out between register and carry flag
Or bit shifted out is shifted in at other end. fairly rare.
* Unsigned integer mul/divide.
Roll shift - ROR ROL - unsigned multiply/divide
Variation of circular and logical shifts, adds use of carry/borrow bit.
Shifted in and out between register and carry flag
Or bit shifted out is shifted in at other end. fairly rare.
* Unsigned integer mul/divide.

 Arithmetic shift - signed multiply/divide
zero shifted in (or carry flag on some systems)
high bit (sign) kept as is
2nd highest bit -> overflow
# If carry flag zeroed before shift,
circular shift can be used for arithmetic shift.
Arithmetic shift - signed multiply/divide
zero shifted in (or carry flag on some systems)
high bit (sign) kept as is
2nd highest bit -> overflow
# If carry flag zeroed before shift,
circular shift can be used for arithmetic shift.

 Barrel shifter.
provides the ability to multiple shifts in a single action.
Commonly used in hardware floating point math to align significands
in single clock cycle.
Logical shift
Barrel shifter.
provides the ability to multiple shifts in a single action.
Commonly used in hardware floating point math to align significands
in single clock cycle.
Logical shift
 Calculating Circuits - Adder
a. Half-adder - adds 1 bit from each number together
Calculating Circuits - Adder
a. Half-adder - adds 1 bit from each number together

