Back
Next
Technique : Manchester encoding
 Change in middle of bit
if zero, one direction,
if one, then the opposite.
Improper wiring can invert bits.
Change guarantees timing. Frequency 2x data transmission.
Manchester encoding is used in wired (10/100) 10Base T Ethernet 802.3
No DC component - average transfer of current is zero.
Allows for isolated coupling
Capacitor, isoloation tranformer, LED/sensor.
Like NRZ but based on change rather than level.
Not well suited for high data rates.
Used in :
10Base-T Ethernet (802.3). (10 Mbit)
Consumer IR (remote controls). Manchester encoding over Infra-red carrier.
RFID or radio frequency identifiers
Technique : Differential Manchester encoding
Change in middle of bit
if zero, one direction,
if one, then the opposite.
Improper wiring can invert bits.
Change guarantees timing. Frequency 2x data transmission.
Manchester encoding is used in wired (10/100) 10Base T Ethernet 802.3
No DC component - average transfer of current is zero.
Allows for isolated coupling
Capacitor, isoloation tranformer, LED/sensor.
Like NRZ but based on change rather than level.
Not well suited for high data rates.
Used in :
10Base-T Ethernet (802.3). (10 Mbit)
Consumer IR (remote controls). Manchester encoding over Infra-red carrier.
RFID or radio frequency identifiers
Technique : Differential Manchester encoding
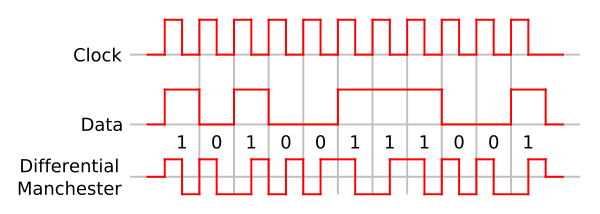 At least one change per clock cycle.
Change at transition if next bit 0.
Change in middle of bit every time. (clock)
* look closely at the digital version of FM. They are essentially
the same except FM always changes at start of bit and
differential Manchester shifts in middle of bit.
This is similar in behavior to NRZI combined with a clock signal.
Zero average DC voltage - because switching guaranteed at least every
2 clock cycles, average voltage zero - more efficient, less susceptible
to noise.
Bits still correct with improper wiring.
1 bit transmitted every 2 clock changes. (2x)
Used on IBM Token ring.
Some types of magnetic and optical storage.
A variation used on magnetic stripe cards (credit cards, etc.)
Used on the 1st floppy drives.
Replaced by MFM - higher density.
At least one change per clock cycle.
Change at transition if next bit 0.
Change in middle of bit every time. (clock)
* look closely at the digital version of FM. They are essentially
the same except FM always changes at start of bit and
differential Manchester shifts in middle of bit.
This is similar in behavior to NRZI combined with a clock signal.
Zero average DC voltage - because switching guaranteed at least every
2 clock cycles, average voltage zero - more efficient, less susceptible
to noise.
Bits still correct with improper wiring.
1 bit transmitted every 2 clock changes. (2x)
Used on IBM Token ring.
Some types of magnetic and optical storage.
A variation used on magnetic stripe cards (credit cards, etc.)
Used on the 1st floppy drives.
Replaced by MFM - higher density.
 Change in middle of bit
if zero, one direction,
if one, then the opposite.
Improper wiring can invert bits.
Change guarantees timing. Frequency 2x data transmission.
Manchester encoding is used in wired (10/100) 10Base T Ethernet 802.3
No DC component - average transfer of current is zero.
Allows for isolated coupling
Capacitor, isoloation tranformer, LED/sensor.
Like NRZ but based on change rather than level.
Not well suited for high data rates.
Used in :
10Base-T Ethernet (802.3). (10 Mbit)
Consumer IR (remote controls). Manchester encoding over Infra-red carrier.
RFID or radio frequency identifiers
Technique : Differential Manchester encoding
Change in middle of bit
if zero, one direction,
if one, then the opposite.
Improper wiring can invert bits.
Change guarantees timing. Frequency 2x data transmission.
Manchester encoding is used in wired (10/100) 10Base T Ethernet 802.3
No DC component - average transfer of current is zero.
Allows for isolated coupling
Capacitor, isoloation tranformer, LED/sensor.
Like NRZ but based on change rather than level.
Not well suited for high data rates.
Used in :
10Base-T Ethernet (802.3). (10 Mbit)
Consumer IR (remote controls). Manchester encoding over Infra-red carrier.
RFID or radio frequency identifiers
Technique : Differential Manchester encoding
 At least one change per clock cycle.
Change at transition if next bit 0.
Change in middle of bit every time. (clock)
* look closely at the digital version of FM. They are essentially
the same except FM always changes at start of bit and
differential Manchester shifts in middle of bit.
This is similar in behavior to NRZI combined with a clock signal.
Zero average DC voltage - because switching guaranteed at least every
2 clock cycles, average voltage zero - more efficient, less susceptible
to noise.
Bits still correct with improper wiring.
1 bit transmitted every 2 clock changes. (2x)
Used on IBM Token ring.
Some types of magnetic and optical storage.
A variation used on magnetic stripe cards (credit cards, etc.)
Used on the 1st floppy drives.
Replaced by MFM - higher density.
At least one change per clock cycle.
Change at transition if next bit 0.
Change in middle of bit every time. (clock)
* look closely at the digital version of FM. They are essentially
the same except FM always changes at start of bit and
differential Manchester shifts in middle of bit.
This is similar in behavior to NRZI combined with a clock signal.
Zero average DC voltage - because switching guaranteed at least every
2 clock cycles, average voltage zero - more efficient, less susceptible
to noise.
Bits still correct with improper wiring.
1 bit transmitted every 2 clock changes. (2x)
Used on IBM Token ring.
Some types of magnetic and optical storage.
A variation used on magnetic stripe cards (credit cards, etc.)
Used on the 1st floppy drives.
Replaced by MFM - higher density.