Back
Lectures
Bus hierarchy
Early systems had a single bus design with 1 speed.
Speed coupled to CPU speed.
Because the speed difference between CPU, memory, and i/o have widened
Newer systems use multiple and/or tiered buses.
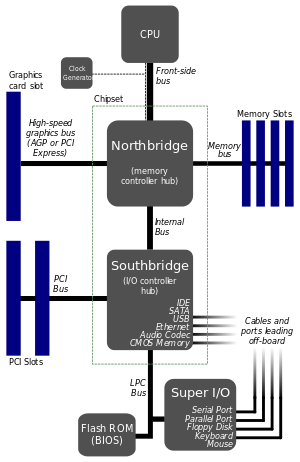
Processor bus (back side bus)
 Connects CPU to L2 cache memory and bus interface.
Originally adjacent to CPU
now implemented on the CPU chip itself at CPU speed.
interfaces with the L1/L2 cache.
Bus width 256/512 bits.
Often proprietary. (Intel chipsets)
Now commonly internal to CPU.
Minimal handshaking because of dedicated use and synchronization.
Front side bus - extremely short, wide CPU interface.
Connects to primary high speed interface controller such as North bridge
circa 2000s
Which in turn, provides separate buses to :
Main memory.
Video interface - AGP
PCIe - faster SATA controllers, Video card, Gigabit Ethernet.
I/O controller chip for moderate speed devices/interface :
South-bridge
Which in turn, interfaces with :
IDE (legacy) bus
SATA/parallel ATA controller
USB controller
Ethernet
Super I/O controller
Which may provide ports for :
RS 232 serial
Legacy printer
Keyboard/mouse
Connects CPU to L2 cache memory and bus interface.
Originally adjacent to CPU
now implemented on the CPU chip itself at CPU speed.
interfaces with the L1/L2 cache.
Bus width 256/512 bits.
Often proprietary. (Intel chipsets)
Now commonly internal to CPU.
Minimal handshaking because of dedicated use and synchronization.
Front side bus - extremely short, wide CPU interface.
Connects to primary high speed interface controller such as North bridge
circa 2000s
Which in turn, provides separate buses to :
Main memory.
Video interface - AGP
PCIe - faster SATA controllers, Video card, Gigabit Ethernet.
I/O controller chip for moderate speed devices/interface :
South-bridge
Which in turn, interfaces with :
IDE (legacy) bus
SATA/parallel ATA controller
USB controller
Ethernet
Super I/O controller
Which may provide ports for :
RS 232 serial
Legacy printer
Keyboard/mouse
 Tiered bus currently being replaced by a hub chip,
allowing each interface a private port at custom speed.
Open standard HyperTransport and Intel Quick-path Interconnect
In these models, the memory controller is on the CPU chip.
CPU->memory controller
\->HyperTransport or Intel Quick-Path->I/O devices.
The connections to the I/O devices are treated as single point to point
connections using network packet communications using one or more
lanes.
HyperTransport
- HyperTransport Consortium (2001) * Lightning Data Transport(LDT)
Used by AMD and others.
Uses packet driven transmission.
Open protocol.
Uses point to point interface between interconnected devices.
HyperTransport controller acts as a router hub.
Used as :
North-bridge replacement.
Interconnect for cache shared by multiple CPUs (L3?).
Multiprocessor interconnect.
Router/switch (10GB Ethernet, WiGig, etch.)
Co-processor interconnect, FPGA, Graphics, etc.
Supports add-on connectors, HyperTransport eXpansion - HTX, HTX3
Allowing add-on cards to access controller chip.
Intel Quick-Path
Intel - (2003) - Intel equivalent of HyperTransport.
Tiered bus currently being replaced by a hub chip,
allowing each interface a private port at custom speed.
Open standard HyperTransport and Intel Quick-path Interconnect
In these models, the memory controller is on the CPU chip.
CPU->memory controller
\->HyperTransport or Intel Quick-Path->I/O devices.
The connections to the I/O devices are treated as single point to point
connections using network packet communications using one or more
lanes.
HyperTransport
- HyperTransport Consortium (2001) * Lightning Data Transport(LDT)
Used by AMD and others.
Uses packet driven transmission.
Open protocol.
Uses point to point interface between interconnected devices.
HyperTransport controller acts as a router hub.
Used as :
North-bridge replacement.
Interconnect for cache shared by multiple CPUs (L3?).
Multiprocessor interconnect.
Router/switch (10GB Ethernet, WiGig, etch.)
Co-processor interconnect, FPGA, Graphics, etc.
Supports add-on connectors, HyperTransport eXpansion - HTX, HTX3
Allowing add-on cards to access controller chip.
Intel Quick-Path
Intel - (2003) - Intel equivalent of HyperTransport.
 From : en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_QuickPath_Interconnect
Core refers to the part of the physical chip that contains :
ALU
command decoder and scheduler
level 1/level 2 caches,
branch predictor,
etc. (datapath circuits).
Uncore (system agent) refers to part of CPU chip that not the
processing core
interfaces with/controls :
level 3 cache - handle cache coherency between cores.
Memory controller
Quick Path Interconnect
(controller for interfacing with PCI/PCIe and other buses).
From : en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_QuickPath_Interconnect
Core refers to the part of the physical chip that contains :
ALU
command decoder and scheduler
level 1/level 2 caches,
branch predictor,
etc. (datapath circuits).
Uncore (system agent) refers to part of CPU chip that not the
processing core
interfaces with/controls :
level 3 cache - handle cache coherency between cores.
Memory controller
Quick Path Interconnect
(controller for interfacing with PCI/PCIe and other buses).
 Connects CPU to L2 cache memory and bus interface.
Originally adjacent to CPU
now implemented on the CPU chip itself at CPU speed.
interfaces with the L1/L2 cache.
Bus width 256/512 bits.
Often proprietary. (Intel chipsets)
Now commonly internal to CPU.
Minimal handshaking because of dedicated use and synchronization.
Front side bus - extremely short, wide CPU interface.
Connects to primary high speed interface controller such as North bridge
circa 2000s
Which in turn, provides separate buses to :
Main memory.
Video interface - AGP
PCIe - faster SATA controllers, Video card, Gigabit Ethernet.
I/O controller chip for moderate speed devices/interface :
South-bridge
Which in turn, interfaces with :
IDE (legacy) bus
SATA/parallel ATA controller
USB controller
Ethernet
Super I/O controller
Which may provide ports for :
RS 232 serial
Legacy printer
Keyboard/mouse
Connects CPU to L2 cache memory and bus interface.
Originally adjacent to CPU
now implemented on the CPU chip itself at CPU speed.
interfaces with the L1/L2 cache.
Bus width 256/512 bits.
Often proprietary. (Intel chipsets)
Now commonly internal to CPU.
Minimal handshaking because of dedicated use and synchronization.
Front side bus - extremely short, wide CPU interface.
Connects to primary high speed interface controller such as North bridge
circa 2000s
Which in turn, provides separate buses to :
Main memory.
Video interface - AGP
PCIe - faster SATA controllers, Video card, Gigabit Ethernet.
I/O controller chip for moderate speed devices/interface :
South-bridge
Which in turn, interfaces with :
IDE (legacy) bus
SATA/parallel ATA controller
USB controller
Ethernet
Super I/O controller
Which may provide ports for :
RS 232 serial
Legacy printer
Keyboard/mouse
 Tiered bus currently being replaced by a hub chip,
allowing each interface a private port at custom speed.
Open standard HyperTransport and Intel Quick-path Interconnect
In these models, the memory controller is on the CPU chip.
CPU->memory controller
\->HyperTransport or Intel Quick-Path->I/O devices.
The connections to the I/O devices are treated as single point to point
connections using network packet communications using one or more
lanes.
HyperTransport
- HyperTransport Consortium (2001) * Lightning Data Transport(LDT)
Used by AMD and others.
Uses packet driven transmission.
Open protocol.
Uses point to point interface between interconnected devices.
HyperTransport controller acts as a router hub.
Used as :
North-bridge replacement.
Interconnect for cache shared by multiple CPUs (L3?).
Multiprocessor interconnect.
Router/switch (10GB Ethernet, WiGig, etch.)
Co-processor interconnect, FPGA, Graphics, etc.
Supports add-on connectors, HyperTransport eXpansion - HTX, HTX3
Allowing add-on cards to access controller chip.
Intel Quick-Path
Intel - (2003) - Intel equivalent of HyperTransport.
Tiered bus currently being replaced by a hub chip,
allowing each interface a private port at custom speed.
Open standard HyperTransport and Intel Quick-path Interconnect
In these models, the memory controller is on the CPU chip.
CPU->memory controller
\->HyperTransport or Intel Quick-Path->I/O devices.
The connections to the I/O devices are treated as single point to point
connections using network packet communications using one or more
lanes.
HyperTransport
- HyperTransport Consortium (2001) * Lightning Data Transport(LDT)
Used by AMD and others.
Uses packet driven transmission.
Open protocol.
Uses point to point interface between interconnected devices.
HyperTransport controller acts as a router hub.
Used as :
North-bridge replacement.
Interconnect for cache shared by multiple CPUs (L3?).
Multiprocessor interconnect.
Router/switch (10GB Ethernet, WiGig, etch.)
Co-processor interconnect, FPGA, Graphics, etc.
Supports add-on connectors, HyperTransport eXpansion - HTX, HTX3
Allowing add-on cards to access controller chip.
Intel Quick-Path
Intel - (2003) - Intel equivalent of HyperTransport.
 From : en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_QuickPath_Interconnect
Core refers to the part of the physical chip that contains :
ALU
command decoder and scheduler
level 1/level 2 caches,
branch predictor,
etc. (datapath circuits).
Uncore (system agent) refers to part of CPU chip that not the
processing core
interfaces with/controls :
level 3 cache - handle cache coherency between cores.
Memory controller
Quick Path Interconnect
(controller for interfacing with PCI/PCIe and other buses).
From : en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_QuickPath_Interconnect
Core refers to the part of the physical chip that contains :
ALU
command decoder and scheduler
level 1/level 2 caches,
branch predictor,
etc. (datapath circuits).
Uncore (system agent) refers to part of CPU chip that not the
processing core
interfaces with/controls :
level 3 cache - handle cache coherency between cores.
Memory controller
Quick Path Interconnect
(controller for interfacing with PCI/PCIe and other buses).